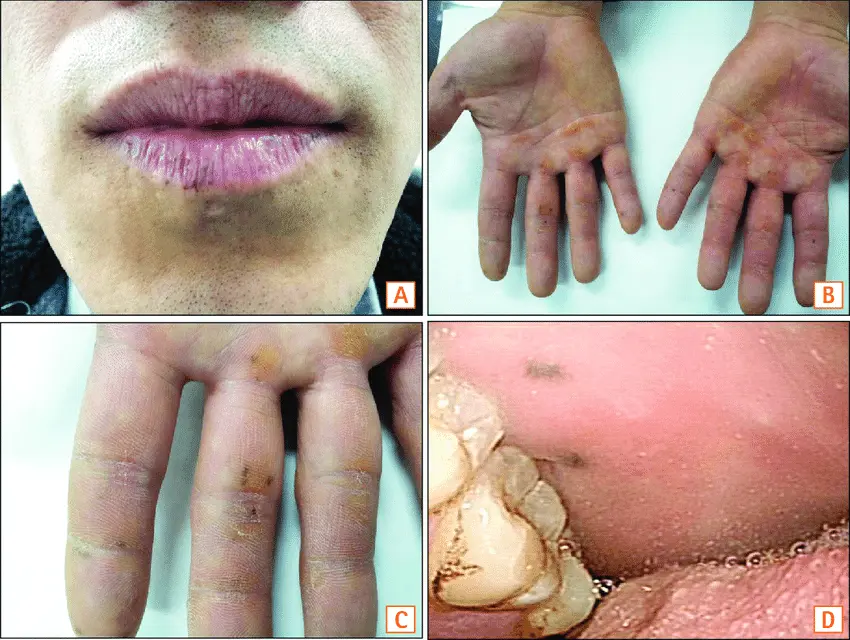
is a rare genetic disorder that can significantly impact the health and quality of life of individuals if not diagnosed and managed early. Characterized by the development of hamartomatous polyps in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and distinctive pigmented spots on the skin and mucous membranes, PJS also increases the risk of certain types of cancer. Diagnosing this condition accurately and early is essential for preventive care and effective monitoring.
In this article, we explore how Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is diagnosed, from clinical signs and family history to advanced genetic testing.
The initial diagnosis of PJS often starts with recognizing visible and symptomatic indicators:
-
Mucocutaneous Pigmentation:
These are dark blue to dark brown freckle-like spots that typically appear around the lips, inside the mouth, on fingers, toes, and sometimes on the skin around the eyes or nose. They often appear in early childhood and can fade with age, but are a key diagnostic clue.
-
Gastrointestinal Symptoms:
Individuals may experience abdominal pain, vomiting, or gastrointestinal bleeding due to polyps. Intussusception a condition where a part of the intestine folds into another section is also common, especially in children, and can be life-threatening if untreated.
To confirm a diagnosis, physicians usually recommend a combination of the following tests:
These imaging tests allow doctors to visually examine the stomach, small intestine, and colon for the presence of polyps. If found, a biopsy is often taken for histological analysis.Read more
A non-invasive diagnostic tool where the patient swallows a tiny camera in a capsule. This helps visualize areas of the small intestine that are difficult to reach with traditional endoscopes.
3. Imaging Techniques
- CT Scan and MRI may be used to detect complications like intussusception, obstruction, or to evaluate organs for early signs of cancer.
- Ultrasound can be helpful, especially in younger patients or when monitoring specific organs.
One of the most definitive ways to diagnose Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is through genetic testing. The condition is caused by mutations in the STK11 (also known as LKB1) gene, which is a tumor suppressor gene located on chromosome 19.
-
Who Should Get Tested?
Anyone with characteristic symptoms or a family history of PJS should undergo genetic counseling and, if appropriate, testing. -
Benefits of Genetic Testing:
- Confirms the diagnosis
- Helps identify at-risk family members
- Guides personalized surveillance and cancer prevention strategies
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, meaning that a mutation in just one copy of the STK11 gene is sufficient to cause the condition. If one parent has PJS, there is a 50% chance of passing it on to their children. Read more
Understanding family history plays a major role in diagnosis. Genetic counseling is recommended for all families with a known or suspected history of the syndrome.
Early and accurate diagnosis of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome can make a significant difference. Individuals diagnosed with PJS require lifelong surveillance for polyps and an increased risk of cancers, particularly in the pancreas, breast, colon, stomach, ovaries, and cervix.
A comprehensive care plan usually involves:
- Regular endoscopic screenings
- Periodic imaging of at-risk organs
- Coordinated care with gastroenterologists, geneticists, oncologists, and other specialists
Key Takeaways
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a genetic condition with clear diagnostic criteria.
- Visible skin/mucosal pigmentation and gastrointestinal polyps are key clinical features.
- Genetic testing for STK11 mutations offers a clear diagnostic path.
- Early diagnosis enables proactive cancer screening and improved health outcomes.
📞 Need Help or Advice?
If you or a loved one has symptoms of PJS or a family history of the condition, consult a medical professional or genetic counselor. At [www.peutz-jeghers.com/], we aim to empower patients, families, and healthcare providers with reliable information and tools for better care.